今天简要地介绍一下ADS和一个简单的实际例程。ADS就是Automation Device Specification,通过使用Beckhoff的ADS接口可以和一些virtual Automation Device或者是Windows的程序相连。如果安装了TwinCAT3可以在C:\TwinCAT\AdsApi\TcAdsDll\Lib\找到TcAdsDll.lib,这就是我们需要的ADS的lib文件。对于ADS接口,最重要的操作就是READ和WRITE了,以下是API的说明。
long __stdcall AdsSyncWriteReq( AmsAddr* pServerAddr, // Ams address of ADS server
unsigned long indexGroup, // index group in ADS server interface
unsigned long indexOffset, // index offset in ADS server interface
unsigned long length, // count of bytes to write
void* pData // pointer to the client buffer
);__declspec( dllexport )
long __stdcall AdsSyncReadReq( AmsAddr* pAddr, // Ams address of ADS server
unsigned long indexGroup, // index group in ADS server interface
unsigned long indexOffset, // index offset in ADS server interface
unsigned long length, // count of bytes to read
void* pData // pointer to the client buffer
);
先启动TwinCAT XAE(VS 2010)也就是VS 2010,新建一个TwinCAT的Project。在SYSTEM里的License选项里可以点击“Activate 7 Days Trial License”,然后会出现以下的对话框,填入生成的Code就完成了注册,用于开发,我们可以一直“Activate 7 Days Trial License”并可以使用TwinCAT 3的完整功能。
如果我们使用了Beckhoff的EtherCAT的IO模块,并通过Ethernet线和PC相连,我们可以将这个设备和TwinCAT相连,在Solution Explorer里的I/O一栏里,展开它,点击Devices,点鼠标右键,点选Scan就可以连接我们的EtherCAT I/O模块了,如下图所示,也可使用工具栏上的Scan图标。
如果发现有正确连接,就会出现下图的对话框。
点选OK,我们就是Active Free Run了。然后在Solution Explorer会看到Device的信息,如下图所示。
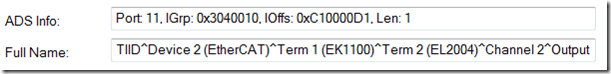
如果我们点选譬如Term 2 (EL2004),并展开它,就会看到这个模块的Channel,如果点击其中一个Channel就会看到上面的I/O,点击这个I/O就会在Variable这个Tab里找到ADS info,如下图所示。
接下来我们就要使用这个ADS Info,并使用上面提到的API对其进行读和写。我们可以在以下链接中找到SAMPLE2(写)和SAMPLE3(读),这两个例程使用了SOFT PLC,提供的PLC可以加载到TwinCAT Project里,这里我们不使用PLC而是直接使用我们上面已经连接好的I/O模块:
http://download.beckhoff.com/download/Software/TwinCAT/TwinCAT3/Samples/TC1000-ADS/ADS/C/
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
#include "C:\TwinCAT\AdsApi\TcAdsDll\Include\TcAdsDef.h"
#include "C:\TwinCAT\AdsApi\TcAdsDll\Include\TcAdsAPI.h"using namespace std;
void main()
{
long nErr, nPort;
AmsAddr Addr;
PAmsAddr pAddr = &Addr;
DWORD dwData;// Open communication port on the ADS router
nPort = AdsPortOpen();
nErr = AdsGetLocalAddress(pAddr);
if (nErr) cerr << "Error: AdsGetLocalAddress: " << nErr << '\n';
pAddr->port = 11;// Read the vlaue of the user, who has to be written to the PLC
cout << "Value: ";
cin >> dwData;//Port: 11, IGrp: 0x3040010, IOffs: 0xC10000D1, Len: 1
nErr = AdsSyncWriteReq( pAddr, 0x3040010, 0xC10000D1, 0x1, &dwData );
if (nErr) cerr << "Error: AdsSyncWriteReq: " << nErr << '\n';// Close the communication port
nErr = AdsPortClose();
if (nErr) cerr << "Error: AdsPortClose: " << nErr << '\n';
}
例程中的代码只需进行两处的改动(红笔处),就可以将我们输入的Data通过ADS接口传递给我们的EtherCAT I/O模块,这里使用的port of ADS server,index group in ADS server interface,index offset in ADS server interface,count of bytes to write,就是我们在上图看到的我们读到的ADS info。对于Read的例程SAMPLE3我就不多加描述了,就是使用AdsSyncReadReq这个API,然后给其相对应的ADS info就行。








没有评论:
发表评论